归并排序
归并排序(Merge sort)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
作为一种典型的分而治之思想的算法应用,归并排序的实现由两种方法:
自上而下的递归(所有递归的方法都可以用迭代重写,所以就有了第 2 种方法);
自下而上的迭代;
算法步骤
申请空间,使其大小为两个已经排序序列之和,该空间用来存放合并后的序列;
设定两个指针,最初位置分别为两个已经排序序列的起始位置;
比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对小的元素放入到合并空间,并移动指针到下一位置;
重复步骤 3 直到某一指针达到序列尾;
将另一序列剩下的所有元素直接复制到合并序列尾。
3. 动图演示
代码实现
JavaScript
function mergeSort(arr) { // 采用自上而下的递归方法
var len = arr.length;
if(len < 2) {
return arr;
}
var middle = Math.floor(len / 2),
left = arr.slice(0, middle),
right = arr.slice(middle);
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
}
function merge(left, right)
{
var result = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result.push(left.shift());
} else {
result.push(right.shift());
}
}
while (left.length)
result.push(left.shift());
while (right.length)
result.push(right.shift());
return result;
}
Python
def mergeSort(arr):
import math
if(len(arr)<2):
return arr
middle = math.floor(len(arr)/2)
left, right = arr[0:middle], arr[middle:]
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right))
def merge(left,right):
result = []
while left and right:
if left[0] <= right[0]:
result.append(left.pop(0))
else:
result.append(right.pop(0));
while left:
result.append(left.pop(0))
while right:
result.append(right.pop(0));
return result
Go
func mergeSort(arr []int) []int {
length := len(arr)
if length < 2 {
return arr
}
middle := length / 2
left := arr[0:middle]
right := arr[middle:]
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right))
}
func merge(left []int, right []int) []int {
var result []int
for len(left) != 0 && len(right) != 0 {
if left[0] <= right[0] {
result = append(result, left[0])
left = left[1:]
} else {
result = append(result, right[0])
right = right[1:]
}
}
for len(left) != 0 {
result = append(result, left[0])
left = left[1:]
}
for len(right) != 0 {
result = append(result, right[0])
right = right[1:]
}
return result
}
Java
public class MergeSort implements IArraySort {
@Override
public int[] sort(int[] sourceArray) throws Exception {
// 对 arr 进行拷贝,不改变参数内容
int[] arr = Arrays.copyOf(sourceArray, sourceArray.length);
if (arr.length < 2) {
return arr;
}
int middle = (int) Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, middle);
int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, middle, arr.length);
return merge(sort(left), sort(right));
}
protected int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) {
int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length];
int i = 0;
while (left.length > 0 && right.length > 0) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result[i++] = left[0];
left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length);
} else {
result[i++] = right[0];
right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length);
}
}
while (left.length > 0) {
result[i++] = left[0];
left = Arrays.copyOfRange(left, 1, left.length);
}
while (right.length > 0) {
result[i++] = right[0];
right = Arrays.copyOfRange(right, 1, right.length);
}
return result;
}
}
PHP
function mergeSort($arr)
{
$len = count($arr);
if ($len < 2) {
return $arr;
}
$middle = floor($len / 2);
$left = array_slice($arr, 0, $middle);
$right = array_slice($arr, $middle);
return merge(mergeSort($left), mergeSort($right));
}
function merge($left, $right)
{
$result = [];
while (count($left) > 0 && count($right) > 0) {
if ($left[0] <= $right[0]) {
$result[] = array_shift($left);
} else {
$result[] = array_shift($right);
}
}
while (count($left))
$result[] = array_shift($left);
while (count($right))
$result[] = array_shift($right);
return $result;
}
C
int min(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? x : y;
}
void merge_sort(int arr[], int len) {
int *a = arr;
int *b = (int *) malloc(len * sizeof(int));
int seg, start;
for (seg = 1; seg < len; seg += seg) {
for (start = 0; start < len; start += seg * 2) {
int low = start, mid = min(start + seg, len), high = min(start + seg * 2, len);
int k = low;
int start1 = low, end1 = mid;
int start2 = mid, end2 = high;
while (start1 < end1 && start2 < end2)
b[k++] = a[start1] < a[start2] ? a[start1++] : a[start2++];
while (start1 < end1)
b[k++] = a[start1++];
while (start2 < end2)
b[k++] = a[start2++];
}
int *temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
if (a != arr) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
b[i] = a[i];
b = a;
}
free(b);
}
递归版:
实例
void merge_sort_recursive(int arr[], int reg[], int start, int end) {
if (start >= end)
return;
int len = end - start, mid = (len >> 1) + start;
int start1 = start, end1 = mid;
int start2 = mid + 1, end2 = end;
merge_sort_recursive(arr, reg, start1, end1);
merge_sort_recursive(arr, reg, start2, end2);
int k = start;
while (start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2)
reg[k++] = arr[start1] < arr[start2] ? arr[start1++] : arr[start2++];
while (start1 <= end1)
reg[k++] = arr[start1++];
while (start2 <= end2)
reg[k++] = arr[start2++];
for (k = start; k <= end; k++)
arr[k] = reg[k];
}
void merge_sort(int arr[], const int len) {
int reg[len];
merge_sort_recursive(arr, reg, 0, len - 1);
}
C++
迭代版:
template<typename T> // 整數或浮點數皆可使用,若要使用物件(class)時必須設定"小於"(<)的運算子功能
void merge_sort(T arr[], int len) {
T *a = arr;
T *b = new T[len];
for (int seg = 1; seg < len; seg += seg) {
for (int start = 0; start < len; start += seg + seg) {
int low = start, mid = min(start + seg, len), high = min(start + seg + seg, len);
int k = low;
int start1 = low, end1 = mid;
int start2 = mid, end2 = high;
while (start1 < end1 && start2 < end2)
b[k++] = a[start1] < a[start2] ? a[start1++] : a[start2++];
while (start1 < end1)
b[k++] = a[start1++];
while (start2 < end2)
b[k++] = a[start2++];
}
T *temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
if (a != arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
b[i] = a[i];
b = a;
}
delete[] b;
}
递归版:
void Merge(vector<int> &Array, int front, int mid, int end) {
// preconditions:
// Array[front...mid] is sorted
// Array[mid+1 ... end] is sorted
// Copy Array[front ... mid] to LeftSubArray
// Copy Array[mid+1 ... end] to RightSubArray
vector<int> LeftSubArray(Array.begin() + front, Array.begin() + mid + 1);
vector<int> RightSubArray(Array.begin() + mid + 1, Array.begin() + end + 1);
int idxLeft = 0, idxRight = 0;
LeftSubArray.insert(LeftSubArray.end(), numeric_limits<int>::max());
RightSubArray.insert(RightSubArray.end(), numeric_limits<int>::max());
// Pick min of LeftSubArray[idxLeft] and RightSubArray[idxRight], and put into Array[i]
for (int i = front; i <= end; i++) {
if (LeftSubArray[idxLeft] < RightSubArray[idxRight]) {
Array[i] = LeftSubArray[idxLeft];
idxLeft++;
} else {
Array[i] = RightSubArray[idxRight];
idxRight++;
}
}
}
void MergeSort(vector<int> &Array, int front, int end) {
if (front >= end)
return;
int mid = (front + end) / 2;
MergeSort(Array, front, mid);
MergeSort(Array, mid + 1, end);
Merge(Array, front, mid, end);
}
C#
public static List<int> sort(List<int> lst) {
if (lst.Count <= 1)
return lst;
int mid = lst.Count / 2;
List<int> left = new List<int>(); // 定义左侧List
List<int> right = new List<int>(); // 定义右侧List
// 以下兩個循環把 lst 分為左右兩個 List
for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++)
left.Add(lst[i]);
for (int j = mid; j < lst.Count; j++)
right.Add(lst[j]);
left = sort(left);
right = sort(right);
return merge(left, right);
}
/// <summary>
/// 合併兩個已經排好序的List
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left">左側List</param>
/// <param name="right">右側List</param>
/// <returns></returns>
static List<int> merge(List<int> left, List<int> right) {
List<int> temp = new List<int>();
while (left.Count > 0 && right.Count > 0) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
temp.Add(left[0]);
left.RemoveAt(0);
} else {
temp.Add(right[0]);
right.RemoveAt(0);
}
}
if (left.Count > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < left.Count; i++)
temp.Add(left[i]);
}
if (right.Count > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < right.Count; i++)
temp.Add(right[i]);
}
return temp;
}
Ruby
def merge list
return list if list.size < 2
pivot = list.size / 2
# Merge
lambda { |left, right|
final = []
until left.empty? or right.empty?
final << if left.first < right.first; left.shift else right.shift end
end
final + left + right
}.call merge(list[0...pivot]), merge(list[pivot..-1])
end
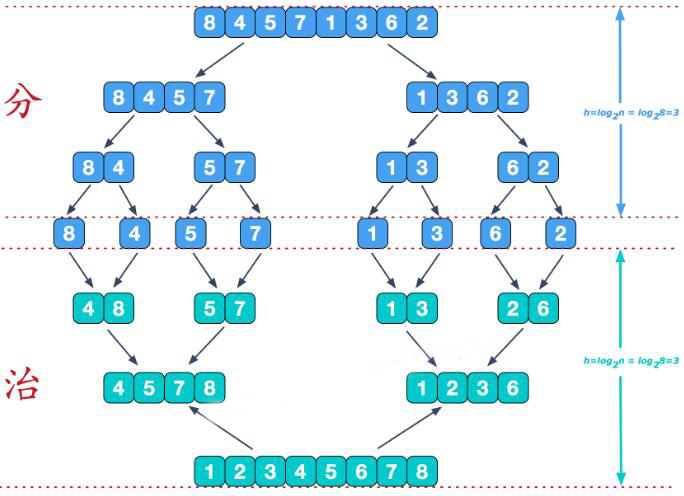
可以看到这种结构很像一棵完全二叉树,本文的归并排序我们采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程,递归深度为log2n。
合并相邻有序子序列
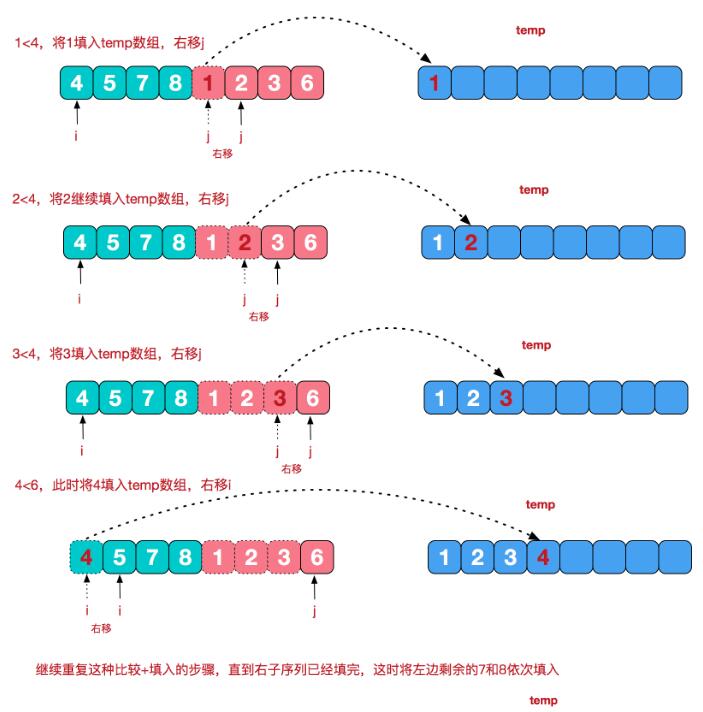
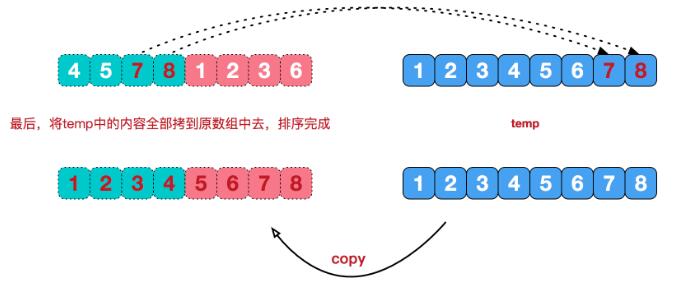
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by chengxiao on 2016/12/8.
*/
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
int []temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){
if(left<right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
sort(arr,left,mid,temp);//左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序
sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);//将两个有序子数组合并操作
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;//左序列指针
int j = mid+1;//右序列指针
int t = 0;//临时数组指针
while (i<=mid && j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while(j<=right){//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
//将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中
while(left <= right){
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}